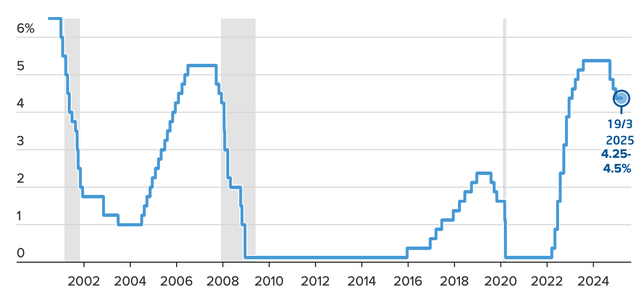
At the end of its second meeting of 2025, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) decided to keep its benchmark interest rate unchanged, although it still indicated that a cut could be made later in the year.
Faced with risks related to tariffs, the Fed’s interest rate adjustment roadmap and slowing economic growth, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) kept its reference interest rate unchanged in the range of 4.25% to 4.5% – the level it has maintained since December. The market also predicted that there was almost no possibility that the US central bank would cut interest rates at this meeting.
In addition to the rate decision, Fed officials updated their forecasts for interest rates and the economy this year and through 2027. The Fed also adjusted the pace of its bond-buying reductions.
Despite the impact of tariffs and fiscal policy on tax cuts and deregulation, officials said they still expect a half-point rate cut by the end of the year. That would put the Fed on track for two cuts this year.
In a statement after the meeting, the monetary policy-making body said the current environment was uncertain. “Uncertainties about the economic outlook have increased,” the FOMC said. “The Committee is mindful of these risks to its dual mandate.”
The Fed pursues a dual goal of maintaining a strong labor market and controlling inflation.
At its meeting, the FOMC lowered its outlook for economic growth and forecast higher inflation. Officials estimated the US economy would grow at a rate of just 1.7% this year, 0.4 percentage points lower than the forecast in December. On the inflation front, the core CPI is expected to rise 2.8%, 0.3 percentage points higher than the previous estimate.
According to the dot plot chart tracking officials’ interest rate expectations, the Fed’s stance has become somewhat more hawkish since December. At the previous meeting, only one FOMC member said that interest rates would not change in 2025, while now there are 4.
The chart shows that officials’ interest rate projections have remained unchanged from December to the following years, with the possibility of making 2 cuts in 2026 and 1 in 2027 to stabilize long-term interest rates at around 3%.

The Fed also said it would continue to scale back its “quantitative tightening” program, gradually reducing the amount of bonds it holds on its balance sheet. The central bank will now allow only $5 billion in government bonds to mature without reinvesting, down from $25 billion previously. However, the Fed kept the $35 billion cap on mortgage-backed securities unchanged.
The Fed’s decision comes after the US stock market was rocked by Washington’s continued tariffs on global trading partners. The uncertainty is also weakening consumer confidence. Retail spending rose in February, albeit less than expected, but key indicators still show that US consumers are weathering the geopolitical storm.
Some cracks have appeared in the labour market. Nonfarm payrolls rose more slowly than estimated in February and a measure of unemployment – which includes the group of disengaged and unproductive workers – rose 0.5% in February to its highest level since October 2021.











